LINE and Mobile Commerce Platform in Japan
20/09/2023
2.71k
We created a mobile application for a multinational conglomerate using LINE, one of Japan’s most popular mobile applications. Nearly 70% of Japanese citizens use the application. This popularity promotes Japanese consumerism by integrating online shopping features within the app. Mobile commerce is obviously on trend throughout Asia.

Transitioning Department Stores to Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce)
We worked with a large conglomerate that works in a multitude of industries in Japan. One such industry is retail. Our client sells daily and household goods in its brick-and-mortar stores. For the longest time, many of its services were exclusive to the physical locations. Mobile commerce (M-Commerce) is a form of e-commerce growing rapidly in Japan. LINE apps, using LIFF (LINE Front End Framework), allow companies to sell their products directly to consumers through the most popular communication application in the country. This article discusses the importance of mobile commerce in Japan and how companies use LINE apps to connect with consumers.
In department stores, consumers can purchase various goods and sign up for membership. In the past, all purchases and membership services were conducted at the physical location. But the consumer landscape continues to shift. Our client noticed the growing popularity M-Commerce amongst the younger generation. They approached us with a proposal to use LINE and bring their business to their customers’ phones and tablets.
LINE in Japan
E-commerce and online shopping are nothing new, and shopping on a smartphone isn’t either. But one of the things the LINE app does well is seamlessly integrate mobile e-commerce into an app that most Japanese people use every day. LINE is the de facto messaging app in Japan.
LINE is similar to WhatsApp, WeChat, or Zalo, with a larger user base than Instagram in Japan. For a while, it fits that niche well. You can add friends and chat with them indefinitely, as long as you have mobile data. But LINE’s ecosystem has grown over the past decade. It behaves more like a complete social networking service (SNS) than the simple chat tool it once was. This means that people are spending more time in the app.
When most people use an application daily, it acts as a primary way to tap directly into their feed. Consumers can follow our client’s brand and receive updates on new products or campaigns. They can purchase items and track their accumulated points, then use them to receive gifts and other perks. They can do all of this without ever leaving the app they use to communicate with their friends and family. It’s one less click away. It’s one less website to visit and one less account to create.

Creating a LINE mini-app Using LIFF
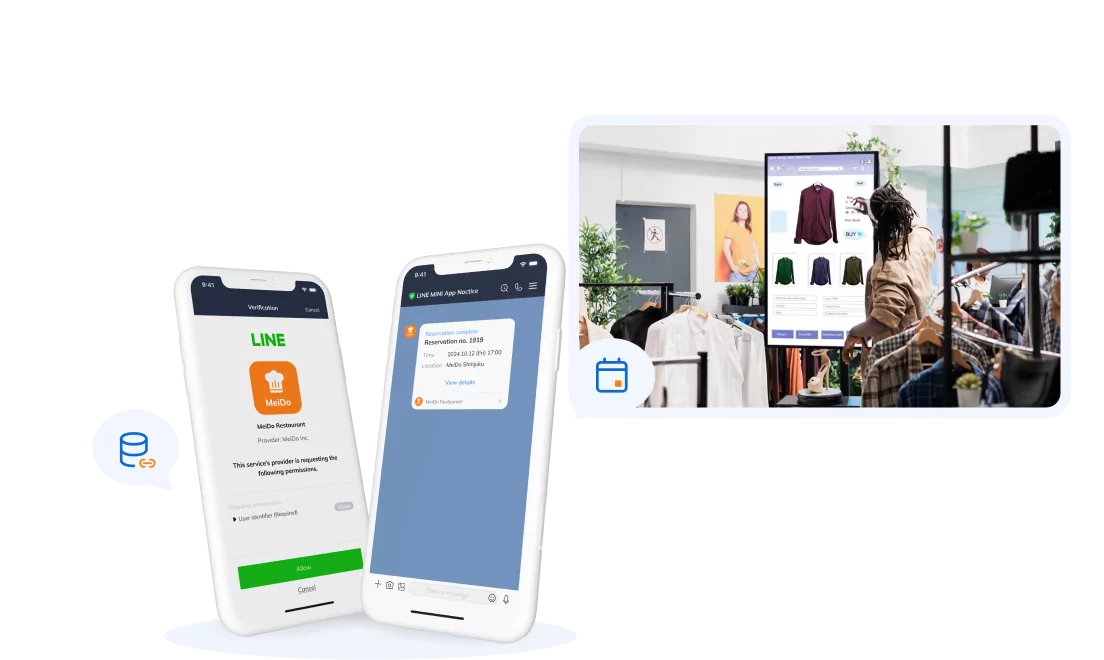
So customers can use LINE to shop online, but what did SupremeTech help build? We used LINE Front-end Framework (LIFF) to create a LINE mini-app for our client to provide their services to customers. LIFF is a web application platform provided by LINE. LIFF apps can receive data from the LINE platform (such as the LINE user ID). They then use this data to provide features that use user data and send messages on behalf of the user.
One of the main features we implemented was the Rich Menu. Rich menus are a staple of LINE and Japanese mobile e-commerce. According to LINE for Business, rich menus are defined as “a menu feature anchored at the bottom of the LINE chat screen. They attract users’ attention by filling a large portion of the screen.” By setting links along with creatives, you can direct users to various other official LINE account features, as well as external sites, reservation pages, and more.” We created this rich menu specifically for our client to promote their services and link directly to their website. From the rich menu, customers can make a points card and access special offers available only to those who follow the client on LINE.
>>> Read more related articles:
- LINE Mini App: Digital Transform Customer Service with Digital Point Cards
- Enhance the Customer Experience on Digital Platforms While Protecting the Legacy for Luxury Brands
Leveling Up Our Technical Expertise
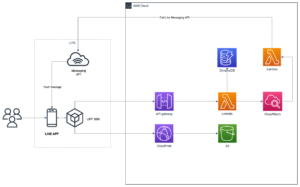
There was one major technical challenge that we faced. This was the first project that SupremeTech completed without using any kind of server. Because the project has so many promotions and various requests, we were asked to complete our first serverless project. In hindsight, it wasn’t a difficult task, but at the time we had to work and develop in a way we were not used to. In this way, this project was a stepping stone for increasing our company’s technical expertise and capabilities.
Technical Stack
Front End: TypeScript (LIFF framework)
Back End: TypeScript
Infrastructure: Serverless architecture with AWS (Lambda, API Gateway, SQS, SNS, DynamoDB, WAF, Cloudwatch Log, .CDK.)