Differences In UX Demands Of A Desktop And Mobile App For A SaaS Product
25/11/2022
1.51k
Table of Contents
While it was more common for individuals and institutions to buy software in the earlier days, the concept of software as a service isn’t that new either. And as smartphones get smarter and more accessible, many product companies are shifting their focus to this ballooning market to sustain and increase profit.
But even though many have increased revenue by enhancing their mobile apps, some companies are excelling thanks to a good desktop app UX. Mobile apps often shine when it comes to daily life products for the individual end user while desktop apps encapsulate stunning collaboration and productivity solutions.
A recent StatCounter study put desktop traffic at 56.51%, with mobile traffic at 50.48%. Many other reports show that there’s still a roughly 60-40 split in mobile and desktop traffic. Both market segments are here to stay, so let’s examine the differences between UX design for desktop and UX design for mobile:
UI Details
One of the significant differences is that desktop users are more comfortable having plenty of items fixed on a single UI screen/window. In contrast, mobile users have limited screen space and may use their thumbs more than any other finger, so you can hardly get away with a cluttered UI.
Not only does it look overwhelming, but it also increases the chances of a user tapping the wrong button/option. Unfortunately, there are no straightforward solutions to this challenge. You’re likely to tuck a feature/function two or more screens away, which users won’t be so happy about.
Luckily, some designs enable you to have retractable menus that slide into place and then slide away. You also have the option to create circular icon menus that appear when you hold down a button for a while. Ultimately, you should have a navigation option that makes it easy to go to the previous page or return to the general menu.
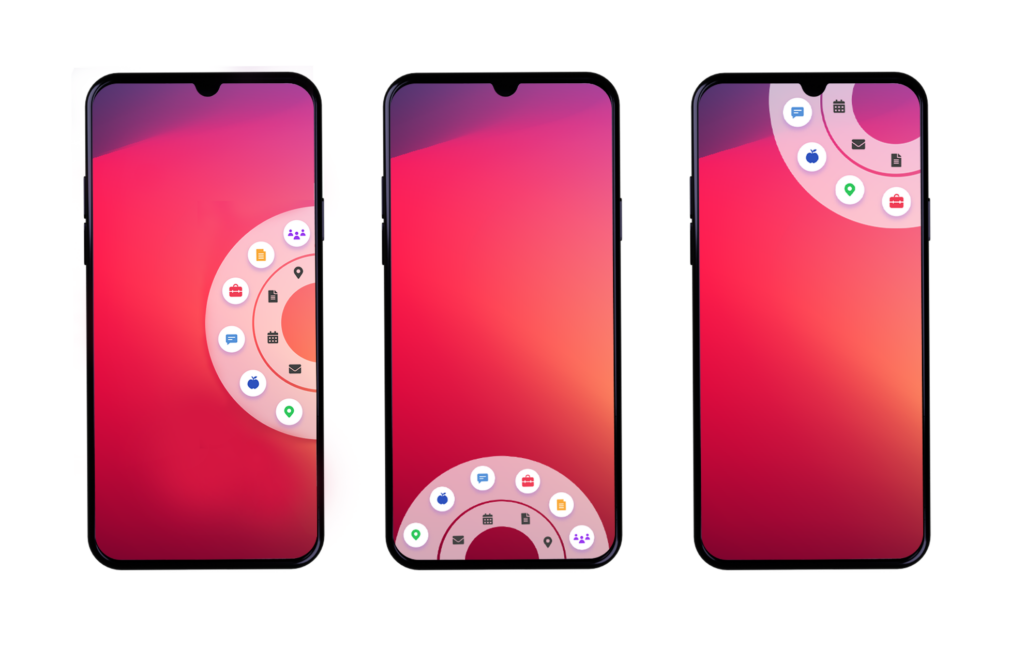

Source: Freepik
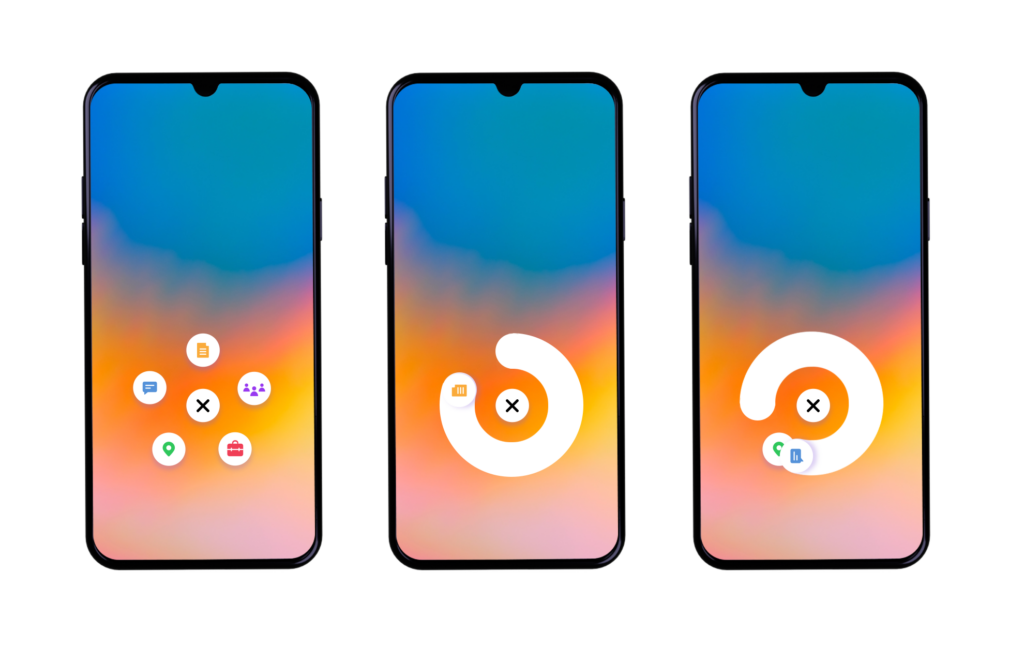

You’ll also need to include a button for the most important action a user can take at that stage in their journey. If it’s the opening page, this could be a signup button; if it’s a category page, it could be an “add to cart” button or a “buy” button if it’s the checkout page. Whatever the CTA is, it should be visible. The user shouldn’t have to first scroll down the page. It should also be within the thumb zone, so ensure it’s wide enough.
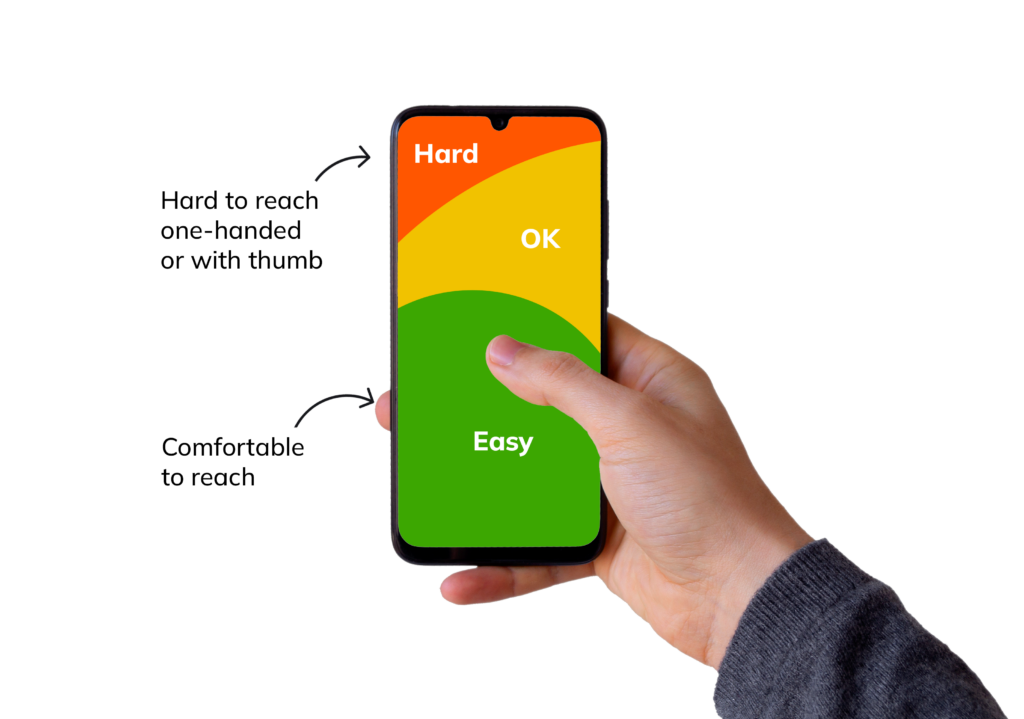
UX design for mobile should also consider the unique gestures like swiping, tilting and shaking that can make a mobile app more fun to use, not forgetting the use of haptic feedback to respond to a user’s command.
>>> Explore more articles about UI and UX design:
- Top 10 Design Tools For UX And UI (2025 GUIDE)
- Top Emerging Trends In App UI Design (2025 OUTLOOK)
- Atomic Design In Software Development
Performance
Ideally, both desktop and mobile app versions should be as smooth and fast as possible. However, when you consider the context in which they operate and the behind-the-scenes work involved in making apps faster, you realize that you might need to put more emphasis on one of them.
Mobile apps are more likely to be run on devices with limited RAM, storage space and processing power. Additionally, users are more likely to travel with mobile devices to remote areas where internet connectivity may be poorer.

This is why it is essential to optimize mobile apps so they can still work fine when low on resources. From memory allocation to caching, reliance on CDNs and compression for lighter media file versions, offline modes, variable streaming bitrates and data template reuse, there are various techniques you can use to achieve higher mobile app performance. Additionally, don’t forget to test on as many devices and OS versions as possible.
Personalization
Many software users want to feel like the product was made just for them and it deeply understands them. In the past, personalization came in the form of changeable skins, fonts and colors. Later, it advanced to more important features like changing languages, currencies and measurement systems.
However, personalization has to evolve even further. For instance, if the user has enabled your mobile app to access their location, can it suggest the perfect playlist when it detects that they are by the beach or at a riverside campsite or safari lodge.
Can your shopping app switch to suggestions for sweaters and cold-weather clothes when the user is in a cold region? Will your food app point them to the places with the best hot beverages and confectioneries? Personalization covers several areas, including the way a person types and uses emojis, the order in which they browse pages, how they use search bars and more.
Unlike desktop apps that run on devices like work computers that stay in the same place and are shared, or laptops that usually move between work and home, a mobile app often runs on a device that spends most of its time with one person, going everywhere. This is why making mobile app versions as adaptable to the user as possible is crucial.
Security and Customer Support
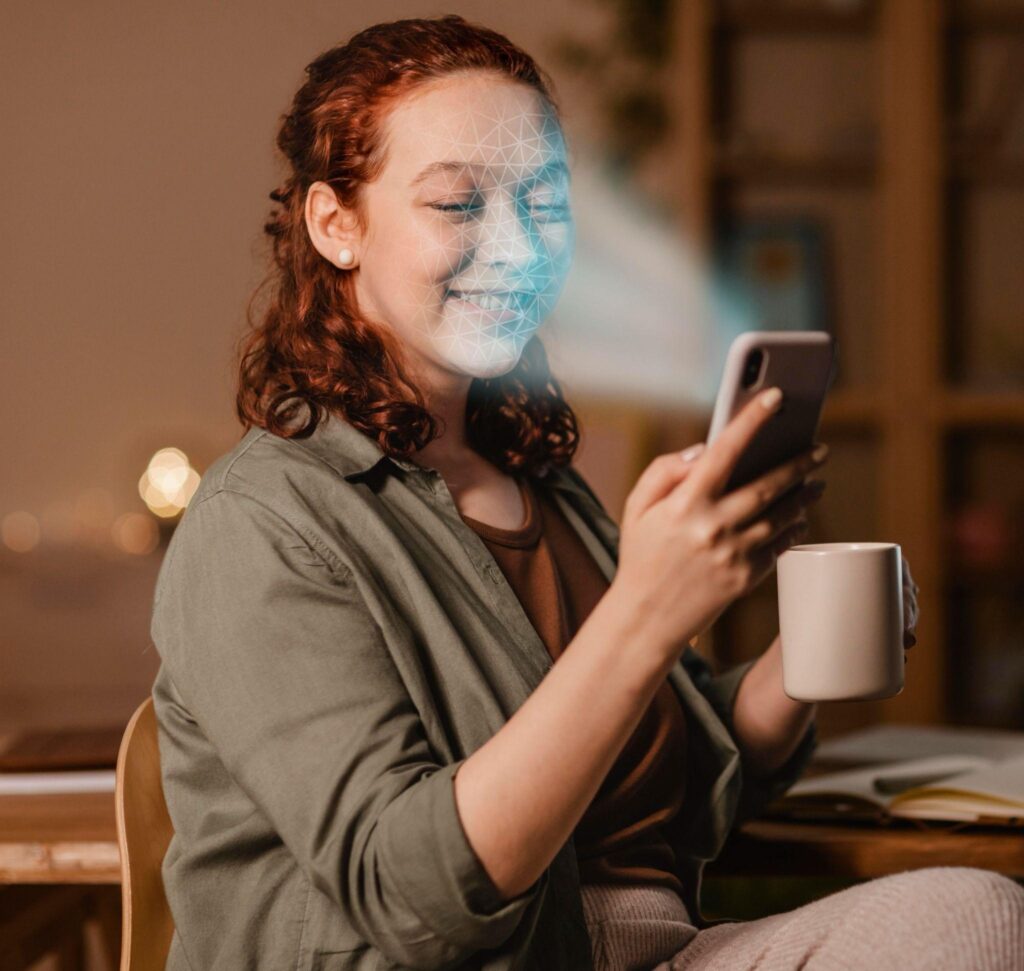
On the security front, mobility creates more headaches since it increases the chances of a user losing a device or connecting to an unsecured public network, among other scenarios. This means you should augment mobile apps with more security options, such as fingerprint locks, face ID and other approaches that a mobile device’s native hardware can allow.
On a deeper level, developers can look into code obfuscation, “root,” and “jailbreak detection ” to further protect against attack techniques that take advantage of the mobile app-specific architectural and operational characteristics.
When it comes to customer support, mobile app UX designers can look into things like the ability to screenshot an error message page and quickly submit it via live chat or tap a call button to speak to an agent.

Another vital customer support area is self-help. Remember, desktop app versions have the advantage since there’s more space to display a help article column alongside the actual screen/dashboard where the user is working. They can also properly display video demos and offer an Info view where you see what a button or other element does by hovering the cursor over it.
That said, mobile app UX designers need to find ways to condense knowledge bases and other self-help materials within the app to simplify the journey from learning to applying. They can also use GIFs to strike a middle-ground between heavy videos and static images when delivering demos.
Wrapping Up
Overall, it’s prudent not to consider the desktop outdated. Instead, focus more on what it easily accommodates, then figure out how to emulate that on mobile devices. As always, it helps to work with a team of professionals conversant with the nuances of developing and delivering desktop and mobile SaaS apps. You can start this journey by contacting the SupremeTech team for a free consultation on how we bring software ideas to life for our clients.
Related Blog